

However, categorizing a palindrome in a nucleic acid sequence (either DNA or RNA) is slightly different. Here, for example, the single difference in the sequences can be eliminated (red for blue or vice versa). For example, AMMA is a typical palindrome in a protein sequence. Repairs can then be made (probably by the mechanism of homologous recombination). All that is needed is to form a loop so that the two sequences line up side-by-side. The RNA sequence UAGCUA is genetic palindrome because, read backwards, it reads AUCGAU, the complement to the original sequence. Sometimes a spacer separates the two inverted. As compared to prokaryotic DNA, the eukaryotic DNA contains a large palindrome of about several thousand base pairs. The length of palindromes may be short by about 3-10 bases or long by about 50-100 base pairs.
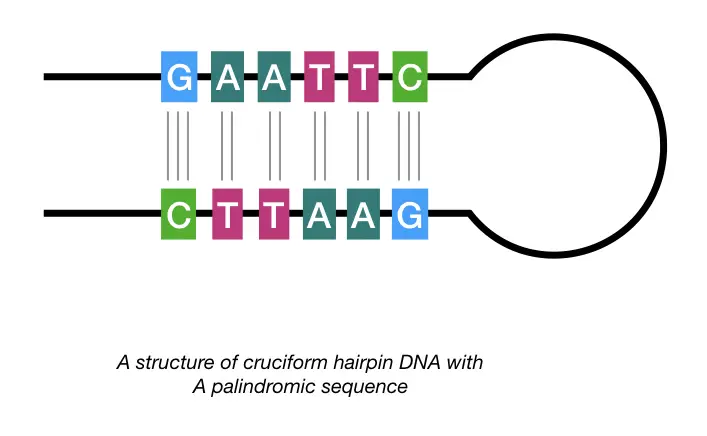
This orientation and redundancy may help ensure that a deleterious mutation in one copy of the set can be repaired using the information in another copy of that set. example, the DNA sequence ACCTAGGT is palindromic because its nucleotide-by-nucleotide complement is TGGATCCA, and reversing the order of the nucleotides in the complement gives the original sequence. The palindromic DNA or palindromes are the inverted repeats and region of dyad symmetry. (The dashes represent the thousands of base pairs that separate adjacent palindromes.) The human Y chromosome contains 7 sets of genes - each set containing from 2 to 6 nearly-identical genes - oriented back-to-back or head-to-head that is, they are inverted repeats like the portion shown here. Inverted repeats at either end of retroviral gene sequences aid in inserting the DNA copy into the DNA of the host.The DNA of many transposons is flanked by inverted repeats such as this one:ĥ' GGCCAGTCACAATGG.~400 nt.CCATTGTGACTGGCC 3'ģ' CCGGTCAGTGTTACC.~400 nt.GGTAACACTGACCGG 5'.For example, the sequence 5'-CGATCG-3' is considered a palindrome since its reverse complement 3'-GCTAGC-5' reads the same. Transcription factors are often dimers of identical proteins homodimers so it is not surprising that each member of the pair needs to "see" the same DNA sequence in the same orientation. For a nucleotide sequence to be considered as a palindrome, its complementary strand must read the same in the opposite direction 2. 5 to 3) on one strand matches the sequence in the opposite direction (e.g. The DNA sequence shown above is that of the glucocorticoid response element where n represents any nucleotide. A palindromic sequence is a nucleic acid sequence in a double-stranded DNA or RNA molecule which when read in a certain direction (e.g. The DNA to which transcription factors bind.In these cases, two different segments of the double helix read the same but in opposite directions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
